What is Hair Loss or Alopecia?
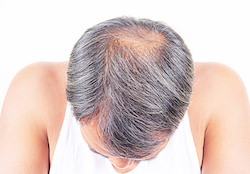
Alopecia is the medical term for hair loss, it is defined as the partial or complete absence of hair in areas of the body where hair normally grows such as the scalp.
According to the American Hair Loss Association, alopecia can be classified into three main types according to the pattern of hair loss:
- Alopecia areata: Hair loss in small patches on the scalp or other parts of the body.
- Alopecia totalis: Hair loss across the entire scalp.
- Alopecia universalis: Hair loss across the entire body.
Who Can Suffer from Alopecia?
According to the American Hair Loss Association, two thirds of men above the age of 35 show signs of hair loss. Although more prominent in men, hair loss is a condition that affects also women starting in in their 50s and 60s. There are various types of hair loss. The most common is androgenetic alopecia, also referred to as male or female pattern baldness.
What are the Causes of Hair Loss?
There are several causes of hair loss. Some causes of hair loss are transient such as stress, pregnancy, nutritional deficiencies, intake of pills containing hormones (e.g. birth control pills), chemotherapy, among others. Other causes of alopecia, such as immune mediated diseases and genetics, can lead to long-term hair loss.
The most common type of hair loss in women is androgenic alopecia, which is caused by an increased in the blood levels of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of the male hormone testosterone. Women who suffer from androgenic alopecia experience diffuse thinning of the hair all over the scalp. On the other hand, men who suffer from androgenic alopecia have distinct patterns of baldness.

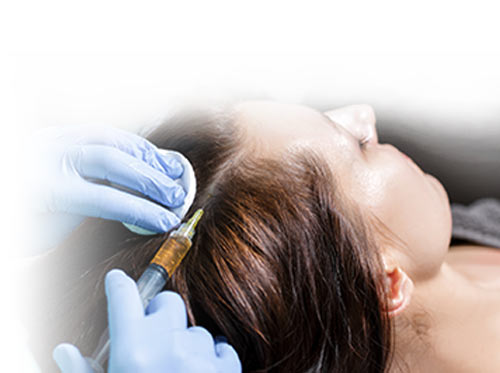
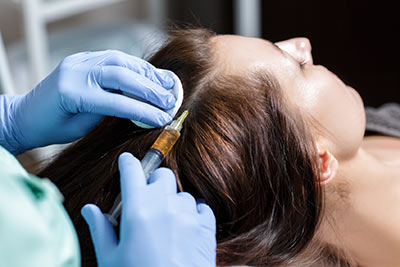
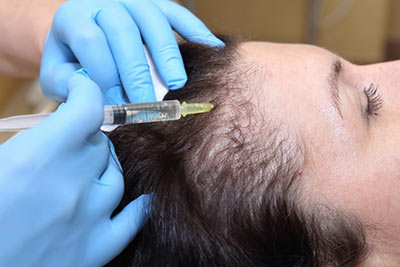 Currently, the most used medical therapies for hair loss include topic solutions of Minoxidil and Triamicinolona, hormone therapies, and hair transplants.
Currently, the most used medical therapies for hair loss include topic solutions of Minoxidil and Triamicinolona, hormone therapies, and hair transplants.